top of page
Machine Learning-based Prediction of Shear Strength & Failure Modes of Interior RC Beam-Column Joints (Studied by Dr Vikas Mehta)

This study explores key factors affecting failure modes and shear strength in interior reinforced concrete beam-column joints (RCBCJs) using a machine learning framework. A dataset of 200 tests was enhanced using PCA and SMOTE to balance failure mode classes. Among five models tested, the Random Forest (RF) algorithm showed the best performance. For shear strength, the RF model achieved R² = 0.99 in training and R² = 0.94 in testing, outperforming ACI 318–14 and EN1998-I:2004. It also achieved 98% accuracy in training and 84% in testing for failure mode classification. SHAP analysis identified column height and beam reinforcement as dominant predictors. A GUI was developed to integrate these insights into practical RCBCJ design.
Regional Earthquake Disaster and Socio-Economic Assessment
(Studied by Sung Hyun Jang, PhD Candidate)

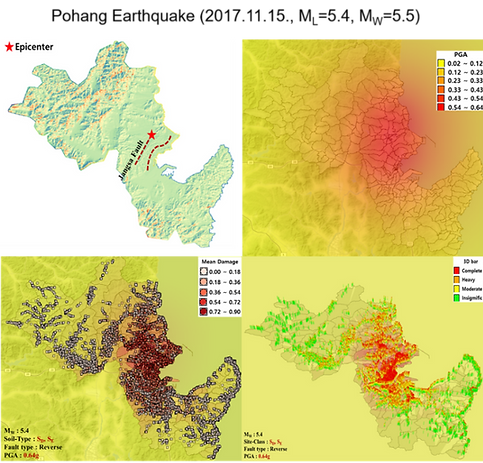
This research addresses a significant limitation in prior South Korean seismic damage analyses, which primarily focused on structural damage assessment while neglecting crucial geological, geotechnical, and broader environmental factors. To bridge this gap, this study undertook a comprehensive examination of seismic damage analysis in Gyeongju City, South Korea.
The analysis incorporated a thorough understanding of the earthquake environment by considering various essential parameters. These included earthquake data such as magnitude and epicenter, along with local factors like fault information and site class. Additionally, the study utilized existing infrastructure data, encompassing structural and occupancy types, to accurately assess the built environment's vulnerability.
The ERGO-EQ platform, a specialized urban seismic damage analysis tool, was employed to process these datasets and evaluate potential damage. This research significantly enhances the understanding of seismic damage analysis at the urban level by integrating geological and geotechnical considerations. It provides valuable insights for practical earthquake response and recovery strategies, thereby aiding informed decision-making for risk mitigation and urban planning.
Artificial Ground Motion Generation Method considering Korean Region Characteristics : A Study based on Gyeongju and Pohang Earthquake Records (Studied by Jin Su Woo, ME)

This study generated artificial earthquake waves using log-normal distribution-based response spectra derived from the 2016 Gyeongju and 2017 Pohang earthquakes. By considering epicenter distance combinations, the artificial waves reflected local seismic characteristics and met domestic design standards. The applied envelope function allowed the waves to realistically simulate amplitude variations and site-specific features.
Rocking & Overturning Properties of Freestanding Contents on Seismically Isolated Building (Studied by Khine Thazin Phyu Kyaw, ME, currently a PhD student at the Univ. of Manchester)

The dynamic behavior of freestanding nonstructural elements such as furniture and other appliances which are resting on the floors were analyzed and evaluated their rocking and overturning characteristics during earthquake excitation. In particular, there is a problem arising from the unclear boundary between rocking and overturning motion of the contents conducted by Ishiyama criterion which has been used in the previous studies.
To solve that problem, a new modified criterion was developed using peak accelerations
(PFAs) and peak velocities (PFVs) of the floors where freestanding contents are located.
For structural analysis, not only fixed base structure (model 1) but also base isolated structure using lead rubber bearings (model 2) and hybrid structure with lead rubber bearings and viscous dampers at the base (model 3) were considered to compare the dynamic behavior of the contents since the structural period was lengthened by the provision of lead rubber bearings.
Running Vibration Properties of Monorail Transit (Daegu City - Line 3)
(Studied by Dong Hee Kwon, ME)

An analysis of the vibrational impact of Daegu Metropolitan Transit lines 1, 2, and 3 is presented, employing acceleration measurements from a proven smartphone application. Measurements of acceleration along three axes were taken, followed by an evaluation and comparison of passenger comfort across the three transit lines, based on the appropriate codes. RMS values from all lines demonstrate acceptable riding comfort levels across the X, Y, and Z axes. Of particular significance, line 1 shows the largest projection on the X-axis (direction of travel), with line 2 and line 3 correspondingly projected onto the Y-axis (lateral) and Z-axis (vertical).
Seismic Isolation & Vibration Control

Seismic isolation and vibration control are essential technologies that reduce the impact of ground motion and vibrations on structures. Using materials like base isolators and dampers, these systems improve resilience during seismic events and dynamic loading. With increasing earthquake frequency and complex structures, their necessity has grown. Vibration control also protects sensitive equipment, ensuring stability and longevity. These technologies enhance safety, reduce maintenance costs, and improve performance under dynamic forces.
Expecially, as a novel structural control strategy, tuned mass damper (TMD) inspired passive and semi-active smart building isolation systems are suggested to reduce structural response and thus mitigate structural damage due to earthquake excitations. The isolated structure’s upper stories can be utilized as a large scaled TMD, and the isolation layer,as a core design point, between the separated upper and lower stories entails the insertion of rubber bearings and (i) viscous dampers (passive) or (ii) resettable devices (semi-active).
Does this sufficiently contribute to urban socio-economic RESILIENCE?

Emphasizing urban-scale earthquake disaster resilience is essential for effective disaster preparedness and recovery. Traditional approaches have primarily focused on enhancing the seismic design and performance of individual structures. Seismic activity, however, frequently causes widespread disruption to entire cities in short timeframes, demonstrating the insufficiency of building-specific strategies.
Urban and regional-level preparedness, including integrated emergency response systems and infrastructure interdependencies, offers a more practical and impactful approach. Resilience-based planning and policy are crucial to guide the recovery phase, encompassing socio-economic effects, ensuring sustainable and adaptive disaster management.
bottom of page